Orthopedic medical billing is far from basic. With complex procedures, multi-stage treatments, and payer-specific documentation rules, orthopedics medical billing requires precision and consistent follow-up. If your practice specializes in orthopedics and struggles with claim denials or inconsistent reimbursements, this guide is for you.
Why Orthopedic Billing Services Need a Specialized Strategy
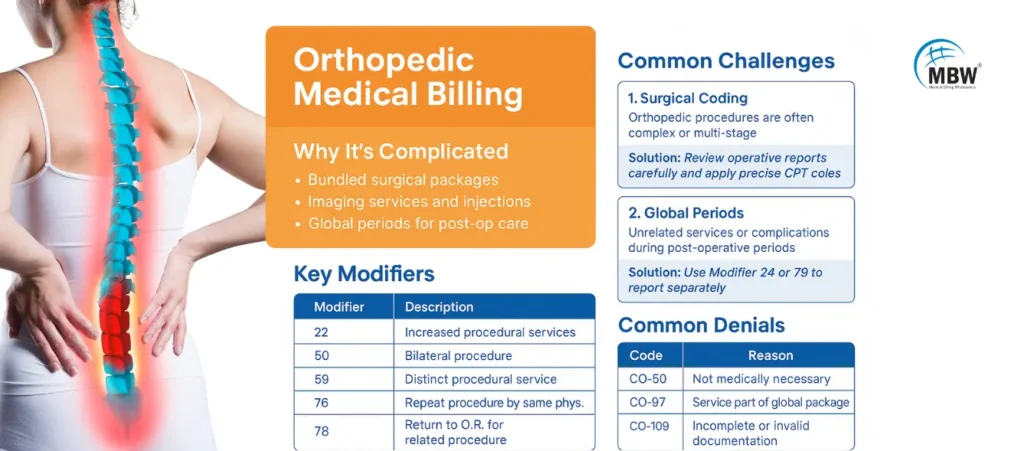
Unlike general specialties, orthopedic billing services involve bundled surgical packages, imaging services, injections, and lengthy global periods. Inaccurate coding or incomplete documentation can delay payments or trigger audits.
In most orthopedic billing companies, claims must reflect:
Exact procedure coding (especially for orthopedic surgery billing)
Appropriate use of modifiers for laterality or repeat procedures
Accurate separation of services during the post-op global period
Learn how we support orthopedic billing and coding services tailored to your specialty.
Common Challenges in Orthopedic Billing and How to Fix Them
1. Complexities in Orthopedic Surgical Coding
Orthopedic surgeries often involve hardware removal, grafting, or multi-site interventions. Each scenario demands precise documentation and code selection. Coders must review operative reports in detail and apply the appropriate CPT codes and modifiers to reflect the full extent of the procedure.
Understanding the correct orthopedic CPT code is essential when billing for major joint surgeries, spine procedures, or fracture care. Even a small error here could significantly reduce reimbursements.
2. Global Period Confusion
The global period includes all routine post-operative care bundled into the initial payment. However, providers often deliver unrelated services or treat new conditions during this window, which must be separately billed. Failure to distinguish these services from routine post-op care leads to denials and loss of revenue.
Modifiers like 24 or 79 must be applied when billing for unrelated procedures or visits during the global period. These indicate to payers that the service is outside the bundled package and eligible for separate reimbursement.
3. Diagnostic Imaging Billing Mistakes
Orthopedic practices frequently depend on diagnostic imaging to guide treatment decisions. Billing errors arise when both the technical and professional components are billed incorrectly—especially when services are outsourced or partially performed in-house.
Coders need to understand when to bill globally and when to use component-based modifiers. Modifier 26 represents the professional interpretation, while TC is used for the technical component. This distinction becomes essential in practices that read but don’t perform the imaging.
4. Inconsistent Documentation for Ortho Billing
Many orthopedic billing companies report that one of the primary reasons for claim rejection is insufficient or inconsistent documentation. Inaccurate coding often stems from discrepancies between what’s documented and what’s billed.
Orthopedic teams should conduct detailed pre-submission audits and regularly communicate with providers to ensure that operative notes and clinical documentation support all coded procedures. When the documentation clearly outlines the complexity and services rendered, claim approvals are more likely.
5. Prior Authorization Gaps
Many orthopedic treatments—like spinal fusions, joint injections, or durable medical equipment—require payer pre-authorization. When this step is skipped or delayed, practices risk denial even after service delivery.
Establishing a payer-specific authorization workflow and training scheduling teams to verify authorization requirements at the time of booking helps ensure that every service rendered is eligible for reimbursement.
Orthopedic Medical Coding: Key Modifiers You Need to Know
| Modifier | Description | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 22 | Increased Procedural Services | Complex shoulder revision surgery |
| 50 | Bilateral Procedure | Bilateral knee arthroscopy |
| 59 | Distinct Procedural Service | Unrelated injection during the same visit |
| 76 | Repeat Procedure by Same Physician | X-ray repeated on same day |
| 78 | Return to OR for Related Procedure | Removal of infected orthopedic implant |
Modifiers help payers understand the relationship between procedures and validate the medical necessity for services billed on the same or subsequent dates.
Most Common Denials in Orthopedic Billing
| Denial Code | Reason | How to Fix |
|---|---|---|
| CO-50 | Not medically necessary | Attach imaging, notes, and patient history |
| CO-97 | Global period conflict | Use Modifiers 24, 25, or 79 with justification |
| CO-109 | Missing/incomplete documentation | Include full operative and imaging reports |
| CO-18 | Duplicate claim | Use internal claim scrubbers and check submission logs |
Denials like these can be mitigated with robust documentation, frequent team training, and proactive denial analysis.
Orthopedic Billing Guidelines Every Practice Should Follow
If your orthopedic practice wants to improve revenue cycle results, follow these core orthopedic billing guidelines:
Verify insurance eligibility and benefits every time
Obtain pre-authorization for surgical procedures and injections
Code procedures based on documentation, not assumptions
Train staff on orthopedic medical billing and modifier use quarterly
Track orthopedic billing KPIs like clean claim rate, denial rate, and AR days
For trustworthy guidelines, explore the educational resources from the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC), a leading nonprofit organization in medical coding and billing.
Conclusion: Why Orthopedic Medical Billing Needs Precision
Orthopedic medical billing isn’t just about entering the right codes—it’s about understanding the complexity behind each procedure, knowing payer-specific rules, and submitting claims with airtight documentation. Whether it’s managing global periods, applying the correct modifiers, or preventing denials, precision is non-negotiable.
“Getting paid in orthopedics isn’t about cracking bones—it’s about cracking the code.”
Get the Help Your Ortho Practice Deserves
Talk to the experts at Medical Billing Wholesalers and see how our orthopedic billing services can reduce denials and improve collections—without adding stress to your staff.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is orthopedic medical billing?
Orthopedic medical billing refers to the process of coding and submitting claims for procedures related to the musculoskeletal system. It includes services like surgeries, imaging, physical therapy, and post-operative care, requiring precise coding and modifier usage.
2. What CPT codes are commonly used in orthopedic billing?
Common orthopedic CPT codes include 20610 (joint injection), 29881 (knee arthroscopy), and 27130 (hip replacement). Coders must carefully select the correct code based on operative notes and follow modifier rules.
3. Why do orthopedic claims get denied frequently?
Frequent reasons include incorrect modifiers, services billed within a global period, missing prior authorizations, or mismatched documentation. Orthopedic billing services reduce these issues through audits and payer-specific rules.
4. Do orthopedic procedures require prior authorization?
Yes, many orthopedic procedures—like joint replacements or spinal surgeries—require prior authorization. Failing to secure it before service can lead to automatic denials.
5. What makes orthopedic billing different from other specialties?
Orthopedic billing involves bundled surgical packages, extended global periods, and high reliance on imaging and assistive devices. These factors make it more complex than general medical billing.
